metal core pcb metal circuit board
-
$1.87≥1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
- Transportation:
- Ocean, Land, Express, Air
- Port:
- shenzhen
Your message must be between 20 to 2000 characters
Contact Now| Supply Ability: | 10000pcs/day |
|---|---|
| Payment Type: | Paypal,T/T |
| Incoterm: | FOB,EXW |
| Transportation: | Ocean,Land,Express,Air |
| Port: | shenzhen |
How is high frequency PCB made?
The circuit board is mainly composed of pads, vias, mounting holes, wires, Electronic Components, connectors, filling, electrical boundaries, etc. The main functions of each component are as follows:
Pad: A metal hole used to solder the pins of components.
Vias: There are metal vias and non-metal vias. Metal vias are used to connect component pins between layers.
Mounting hole: used to fix the circuit board.
Wire: The copper film of the electrical network used to connect the pins of the components.
Connectors: Electronic connectors used to connect between circuit boards.
Filling: Copper coating for ground wire network, which can effectively reduce impedance.
Electrical boundary: used to determine the size of the circuit board, all components on the circuit board cannot exceed the boundary.
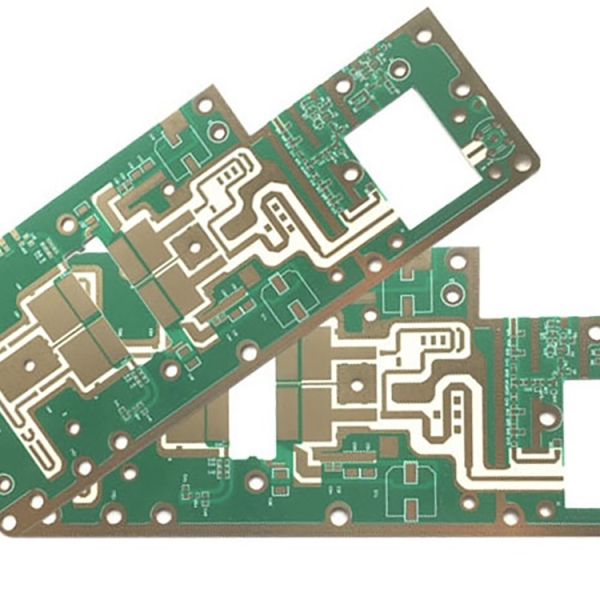
In high-frequency circuit design, the power supply is designed in the form of layers, and in most cases it is much better than the design in the form of a bus, so that the loop can always follow the path with the least impedance. In addition, the power board has to provide a signal loop for all generated and received signals on the PCB, so that the signal loop can be minimized, thereby reducing noise, which is often overlooked by low-frequency circuit designers.
In high-frequency PCB design, we should follow the following principles:
The unity and stability of power supply and ground.
Careful wiring and proper termination can eliminate reflections.
Careful wiring and proper termination can reduce capacitive and inductive crosstalk.
Need to suppress noise to meet EMC requirements.

1. The dielectric loss (Df) must be small, which mainly affects the quality of signal transmission. The smaller the dielectric loss, the smaller the signal loss.
2. Low water absorption and high water absorption will affect the dielectric constant and dielectric loss when damp.
3. The dielectric constant (DK) must be small and stable, usually the smaller the better. The signal transmission rate is inversely proportional to the square root of the material's dielectric constant. High dielectric constant is likely to cause signal transmission delay.
4. Try to be consistent with the thermal expansion coefficient of copper foil, because the inconsistency will cause the copper foil to separate in the cold and heat changes.
5. Other heat resistance, chemical resistance, impact strength, peel strength, etc. must also be good.
In general, high frequency can be defined as the frequency above 1GHz. At present, the most frequently used high frequency is a fluorine dielectric substrate, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which is usually called Teflon.
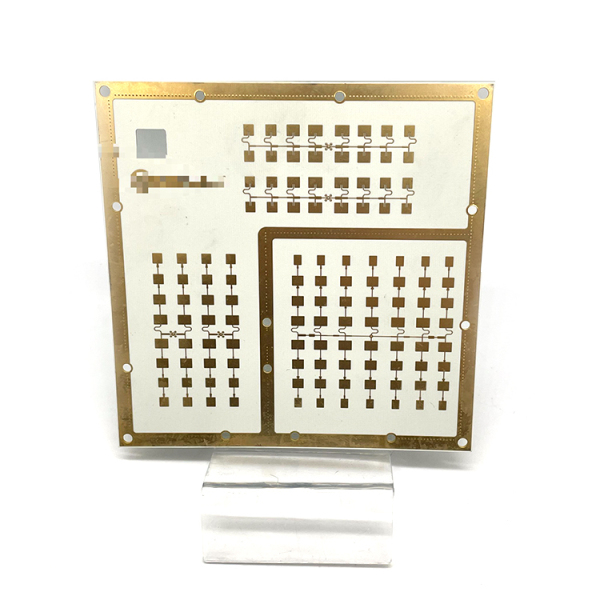
1. The impedance control requirements are relatively strict, and the relative line width control is very strict, with a general tolerance of about 2%.
2. Due to the special plate, the adhesion of PTH copper is not high. It is usually necessary to roughen the vias and the surface with the help of plasma treatment equipment to increase the adhesion of the PTH hole copper and solder mask ink.
3. Do not grind the board before doing solder mask, otherwise the adhesion will be very poor, only use micro-etching potion to roughen it.
4. The plates are mostly polytetrafluoroethylene materials, and there will be a lot of burrs when forming with ordinary milling cutters, and special milling cutters are required.
5. High-frequency circuit board is a special circuit board with higher electromagnetic frequency. Generally speaking, high-frequency can be defined as a frequency above 1GHz.
Its various physical properties, accuracy, and technical parameters require very high requirements, and are often used in automotive anti-collision systems, satellite systems, radio systems and other fields.
Related Keywords